How to Read Blob Data in Db2
Theory of Blob storage in DB2
![]()
Introduction : In real globe we have structured information and unstructured data. Ordinarily we refer to the unstructured data (images,files,mp3,videos) as large objects. Big objects tin can exist saved wihtin a RDBMS in BLOB format. Nigh of the RDMBS like oracle,db2, postgress does support this. In that location is a downside to this, which I volition talk over in detail below along with the behavior and limitations. This is large information handing in the RDBMS world.
Permit me give you a cursory intro into Blobs in DB2 first.
Hulk is brusk for Binary Big Object which tin can be many things — for example, Documents, Vocalisation Data, Pictures, or mixed media. What makes BLOBs unique is that BLOB data is not stored in a row. It'due south stored externally to the table with a pointer giving the location of the object. Check the below image …

Let's leave what'due south been said to a higher place for awhile…and permit's talk over some theory…
At that place are 5 types of table spaces in DB2.
Catalog TBS( There is only one catalog table space per database, and it is created when the CREATE DATABASE command is issued. Named SYSCATSPACE by DB2, the itemize tabular array space),
Regular TBS( A regular table infinite stores all permanent data, including regular tables and indexes. Information technology can also hold large data such as LOBs (Large Objects) unless they are explicitly stored in a large table infinite.)
Big TBS( A big table infinite stores all permanent data just as a regular table space does, including LOBs. This tabular array space type must be DMS, which is the default type. A table created in a large table infinite can be larger than a table in a regular table space. A big table tin support more than 255 rows per data page improving space utilization on data pages.)
System Temp TBS( A system temporary table space stores internal temporary information required during SQL operations such every bit sorting, reorganizing tables, creating indexes, and joining tables)
User Temp TBS( A user temporary table space stores declared global temporary tables.)
Since we are focusing on LOBs here, lets focus but on regular and large tabular array spaces.
Whats a container ? A container is linked to a table-space during creation and this will basically link a deejay storage to the table space. Each table infinite has 1 or more containers. Containers can be added to or dropped from table infinite, and their sizes tin exist modified. Simply said its a path in the server where the information files for the linked table space will be saved.
We tin can create table spaces in different page sizes. Page size defines the size of pages used for the table space. Supported sizes include 4K, 8K, 16K, and 32K. The valid values for integer without the suffix Chiliad are 4 096,8 192, 16 384, or 32 768. (on a non related side note, the page size of the table space and the buffer pool has to be the same)
When defining the Tablespace, folio size limits the row length and column count of tables that tin exist placed in the table space according to the limits shown in Table 1.

Lets dig deep into the details above. What you tin can meet is there is a limit on the row size and the column count based on the page size. Who controls the folio beliefs ? Its the Operating System ?. Like HDFS for Hadoop,Similarly the page size related to some kind of a file organisation in the Bone which DB2 is installed.
When you are creating a tabular array on superlative of a tablespace the page size of information technology logically links to the table. Which ways if we create a table on a tablespace with 4k folio size, this tabular array can accept max 4005 bytes in a single row(based on the table 1). In other words, your table can take x varchar columns with each being 40 in length. (varchar fills the total length of the column even if enter a single grapheme, but varchar2 does not).
Each data blazon has a default way of using infinite and we can use the below SQL to check the infinite taken in past each column.
Select bigint(length(COL_NAME) equally Size_KB from Table_Name;
By now you would empathise that we use BLOB when we feel that the length of the row with the LOB will exceed the base of operations table infinite or the regular tabular array space. To go a improve understanding let's check an actual DDL of a table with a Hulk cavalcade.
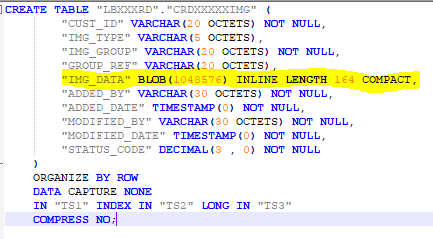
We accept created a table with a blob column and in TS1 regular table infinite,and the LOB column volition be in TS3 LONG table space. I accept come up across the below basic gear up of rules when dealing with BLOB columns.( It took me virtually iv hrs of reading to gear up the same :))
- When a BLOB cavalcade is defined in a db2 tabular array, there has to be a Large table infinite defined at the aforementioned fourth dimension. LOB Object information will be saved in the LARGE table space. LOB object information will be still saved in regular table space of the base table.
side note : if you have two Blob columns y'all need to accept two Large tabular array spaces ideally.
ii. The base of operations tabular array will take a logical link to the LOB Data in Big table infinite. This is chosen LOB Information and it will reside in the regular table infinite.
LOB object information is something like a link to locate the LOB information.
3. If the LOB cavalcade is defined Blob INLINE, then a certain portion of the LOB information is stored in the regular tabular array space. We tin can specify the limit in KB.
(you can read about the LOB INLINE theory from this link : clickme )
Coming back to our context here in the DDL of the table above, as we tin run across, a 164kb limit is given for inline ("IMG_DATA" Blob(1048576) INLINE LENGTH 164 Meaty ). This means a certain portion of LOB data is saved in the regular tabular array space. We tin utilise the below sql to cheque what rows are inline and what rows are not.
select ADMIN_IS_INLINED(img_data) every bit x from crdXXXXXimg society by x desc;
— note : i means its inline
On a side note, using COMPACT fundamental give-and-take does not mean the cavalcade in compressed. You can google on this later.
Say that y'all take a storage group every bit SG1 and both TS1 and TS2 are in it. SG1 is full, and y'all make up one's mind to move the CRDXXXIMG tabular array to a new storage grouping coz it has 900GB.
We tin can understand that , If y'all are facing storage issues then you demand to move both the TS1 and TS3 into a new storage group. Moving TS3 only volition not give you the expected issue of infinite reduction since some of the BLOB information are INLINE and resides in regular table space.
Please go out a comment ! thank you !
Next up : I volition discuss on how to compress data and minimize performance issues in BLOBs.
Likewise I will discuss the possibility of using BigSql in the same application in parallel to db2 sql ,which is a SQL engine congenital ontop of Hadoop file organization/Hive. Merely my question here is on how to minimize storage? If I dont intendance about the operation and I do care only about the disk storage infinite, practise I actually want to waste my time migrating BLOB objects in my DB2 table into a Hadoop file system?
Reference
analytics, D. (2019). Optimize storage with deep compression in DB2 10. [online] Ibm.com. Bachelor at: https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/information/library/techarticle/dm-1205db210compression/index.html [Accessed 27 Mar. 2019].
Ibm.com. (2019). IBM Knowledge Center. [online] Available at: https://world wide web.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/SSEPGG_11.1.0/com.ibm.db2.luw.admin.dbobj.doc/doc/c0054525.html [Accessed 27 Mar. 2019].
Ibm.com. (2019). IBM Knowledge Center. [online] Available at: https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/SSEPEK_11.0.0/perf/src/tpc/db2z_decide2compressdata.html [Accessed 27 Mar. 2019].
Krafick, M. (2019). Attack of the Blob! (Blobs in a Transaction Processing environment). [online] DataGeek.blog. Available at: https://datageek.web log/2013/04/26/attack-of-the-blob-blobs-in-a-transaction-processing-environs/?unapproved=125432&moderation-hash=0a7f7fd431eb569214d7685ac14e23d8#annotate-125432 [Accessed 27 Mar. 2019].
Source: https://medium.datadriveninvestor.com/blob-storage-in-db2-3f0a571747ab
Post a Comment for "How to Read Blob Data in Db2"